INTRODUCTION
Hand and wrist injuries can dramatically affect our lives. As humans, we rely heavily on our hands to manipulate objects, grip, carry and reach for things for our survival. We take for granted the ability to feed ourselves, maintain personal hygiene or use technology and transportation, until we sustain a hand or wrist injury. Given the importance of our hands and their role in facilitating our everyday tasks and activities, it is essential to have your injury or symptoms addressed at the onset of your symptoms.
This article will briefly outline some of the common presentations and give a brief description of how to manage them. It is important to seek the advice and assessment of a Hand Physiotherapist to ensure you are receiving the highest level of care.
WRIST AND HAND ANATOMY
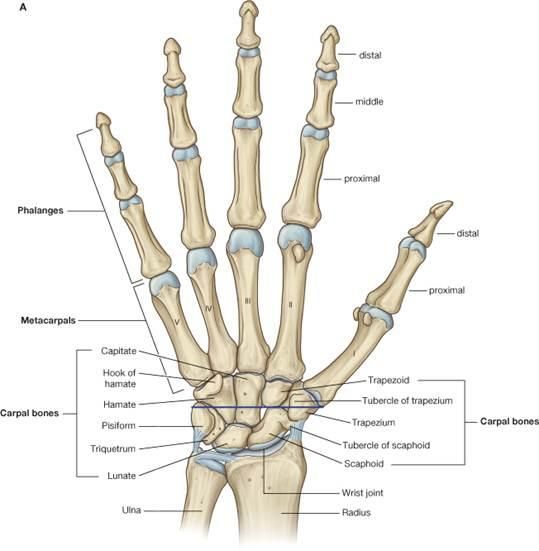
At an anatomical level, the wrist contains many small bones neatly joined together by ligaments. This area is commonly referred to as the Carpus. We have our two main forearm bones, the radius and ulna running from the elbow to the wrist. The other end of the carpus is where our finger and thumb bones join, our metacarpals and the ends of our fingers called phalanges. Our thumb contains a proximal and distal phalanx, and the 2nd to 5th digits contain a proximal, middle and distal phalanx (Figure 1).
Each bone in the carpus has a specific name and the joint spaces between each of these carpal bones is derived from those names – the join between the carpal, scaphoid and lunate is called the scaphoid-lunate joint. We also have a number of tendons and muscles that either traverse the top or bottom of the wrist and or digits and accompanying these are nerves and blood vessels.
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
When considering the types of hand and wrist injuries, we can loosely divide them into two categories – an acute onset or traumatic presentation and a chronic or overuse presentation.
Typically with traumatic or acute injury, we generally feel symptoms immediately and generally, these symptoms immediately follow a particular movement or mechanism of injury.
An overuse or chronic injury, refers to symptoms that have developed over a period of time, whether the symptoms stay the same or gradually change. This article will give a brief overview for each of these categories for most common hand and wrist presentations.
One common mechanism of hand and wrist injuries is falling on an outstretched hand. This is a common occurrence out on the football field, tripping over when walking or coming off a bike. Structures that are commonly injured include:
Each of these structures will require a period of immobilisation in a specific position prior to commencing rehabilitation to restore movement and strength to the hand and wrist.
Wrist pain can also occur after repeating a movement for a prolonged period of time, or vigorous repetitions with force. Some of the conditions that can occur include:
Management of these hand and wrist injuires would typically involve splinting into a specific position for a period of time with regular tendon gliding exercises, icing of the affected area. Once the symptoms have begun to subside, weaning from the splint is introduced and gradual strengthening and movement exercises are prescribed.
When we look at common traumatic hand and wrist injuries to the thumb and digits, the following presentations come to mind:
Each of these hand and wrist injuries require specific positioning for varying periods of time to enable tissue healing and then rehabilitation of movement and strengthening will follow.
Overuse hand and wrist injuries of the extremities include:
Similarly, most of these areas will require splinting for periods of time to ensure protection of the joint surface or rest of the inflamed area. Careful prescription of movement exercises, tendon gliding exercises, icing inflamed areas and controlled strengthening are all likely to be part of the rehabilitation phase.
Whether in an acute or more chronic presentation, depending on the severity, deformity, deviation and integrity of surrounding structures, other measures will be taken to ensure the best outcome for the individual. Some of these things include imaging, cortisone injections, or referral to a Specialist for surgical intervention.
If you have a hand or wrist injury, no matter how little, be sure to put your health first and consult your Hand Physiotherapist today.
About the author: Sophie Halsall-McLennan is a Drysdale based physiotherapist and is the owner of Fresh Start Physiotherapy in Curlewis, Victoria and has a special interest in hand therapy, tennis elbow and back pain. Dr7 Physiotherapy Podiatry Hydrotherapy Massage in Yokine Perth WA is proud to be partnering up with Sophie to provide high quality blogs to help educate the community in regards to health, wellness and physiotherapy.